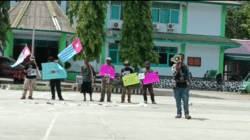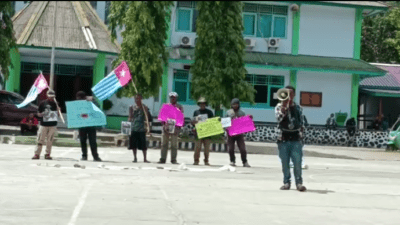Nabire, Jubi – The Indonesian president, Joko ‘Jokowi’ Widodo, is desperate to keep hidden Indonesia’s dark, dirty secret: its brutal 50-year war in its easternmost provinces. Here are five things you should know about Indonesian rule in West Papua:
- It is one of the world’s longest-running military occupations
Indonesia seized West Papua, the western half of the island of New Guinea, in 1963, shortly after the Dutch colonists pulled out. Political parties were immediately banned, nascent Papuan nationalism crushed, and tens of thousands of troops, police and special forces flooded in. In 1969 a UN-supervised sham referendum was held, and just over a thousand hand-picked representatives were bribed, cajoled and threatened into voting in favour of Indonesian rule.
A police state has shackled the vast region ever since, battling a low-level tribal insurgency and suppressing independence aspirations with such vigour that raising the Papuan national flag can land you 15 years in prison.
- It is possible that Indonesian rule constitutes genocide
Although international media and NGOs have been nearly uniformly banned from the territory for decades, most observers estimate that over 100,000 native Papuans have been killed since the 1960s – at least 10% of the population. With echoes of Indonesia’s rule in East Timor, which eliminated around one third of the population, a 2004 report from Yale Law School concluded: “[There is] a strong indication that the Indonesian government has committed genocide against the West Papuans.”
Reports of barbarous killings regularly emerge, and one study recently described torture as a ‘mode of governance’ in the provinces. The abuse tends to be intertwined with projects of resource extraction and ‘transmigration’.
During a military campaign in the early 1980s, the Indonesian army ran under the slogan, ‘Let the rats run into the jungle so that the chickens can breed in the coop’.
In practice, this meant wiping out Papuan villages and bringing in ethnic Indonesians to work on economic projects like Freeport’s giant Grasberg gold and copper mine, which has been accused of ‘ecocide‘ and dumps over 200,000 tonnes of tailings in local river system every day.
The influx of Indonesians has left the original inhabitants a near-minority in the land, struggling to maintain their culture and often nomadic way of life.
- West Papuans overwhelmingly want independence
Even the pro-Indonesian US ambassador admitted in the late 1960s that “possibly 85 to 90%” of West Papuans “are in sympathy with the Free Papua cause.”
Paul Kingsnorth, an investigative reporter who travelled the region in the early 2000s, described the independence campaign as a “broad-based social movement, which almost everyone in West Papua, if you get them alone, will admit to belonging.”
Most West Papuans consider themselves Melanesian, with more in common with darker-skinned Pacific populations than the Indonesians who often treat them as racially inferior. Culturally, linguistically, ethnically – Papuans have little in common with Indonesians.
- The Indonesian state is terrified of international exposure
Alongside barring international media from West Papua, Indonesia runs counter-intelligence operations overseas to neutralize the international independence movement, surveilling and harassing campaigners based in Australia and elsewhere.
Leaked military documents bemoan the success activists have had in “propagating the issue of severe human rights violations in Papua,” and Indonesia has been working hard to ensure exiled Papuan representatives are barred from regional Pacific organisations. Foreign visitors in the provinces are placed under routine surveillance.
- Britain & the West have supported Indonesia’s occupation for decades
Britain’s historic alliance with the Indonesian state dates primarily to General Suharto’s bloody coup in 1965-6. In the midst of the slaughter of at least 500,000 suspected members of the Indonesian Communist Party – which British officials gleefully described as a ‘ruthless terror’ – the Foreign Office argued that “the Generals are going to need all the help they can get”, releasing £1m in aid and granting the export of military equipment. The Indonesian left was duly decimated – never to recover – and the pro-Western Suharto was firmly in control.
Since then, Britain’s support for Indonesian rule in West Papua has been unwavering. Privately recognising the ‘savage’ nature of Indonesian rule, publicly officials have voted to legitimate Indonesian rule at the UN and pledged support for Indonesia’s ‘territorial integrity’.
Until the late 90s, the UK was one of Indonesia’s primary arms suppliers. Kopassus, the Indonesian Special Forces, have been trained and armed by the UK, US and Australia, despite a well-documented record of horrific human rights abuse in Papua. Britain funds and trains Detachment 88, the Indonesian counter-terrorism unit accused of massacres in Papua’s central highlands.(*)
*Written by Connor Woodman, Politics of Papua Project, University of Warwick, UK